‘We didn’t have anybody there’: Kyiv’s troops struggle as Russia advances
 07 January 2025
07 January 2025
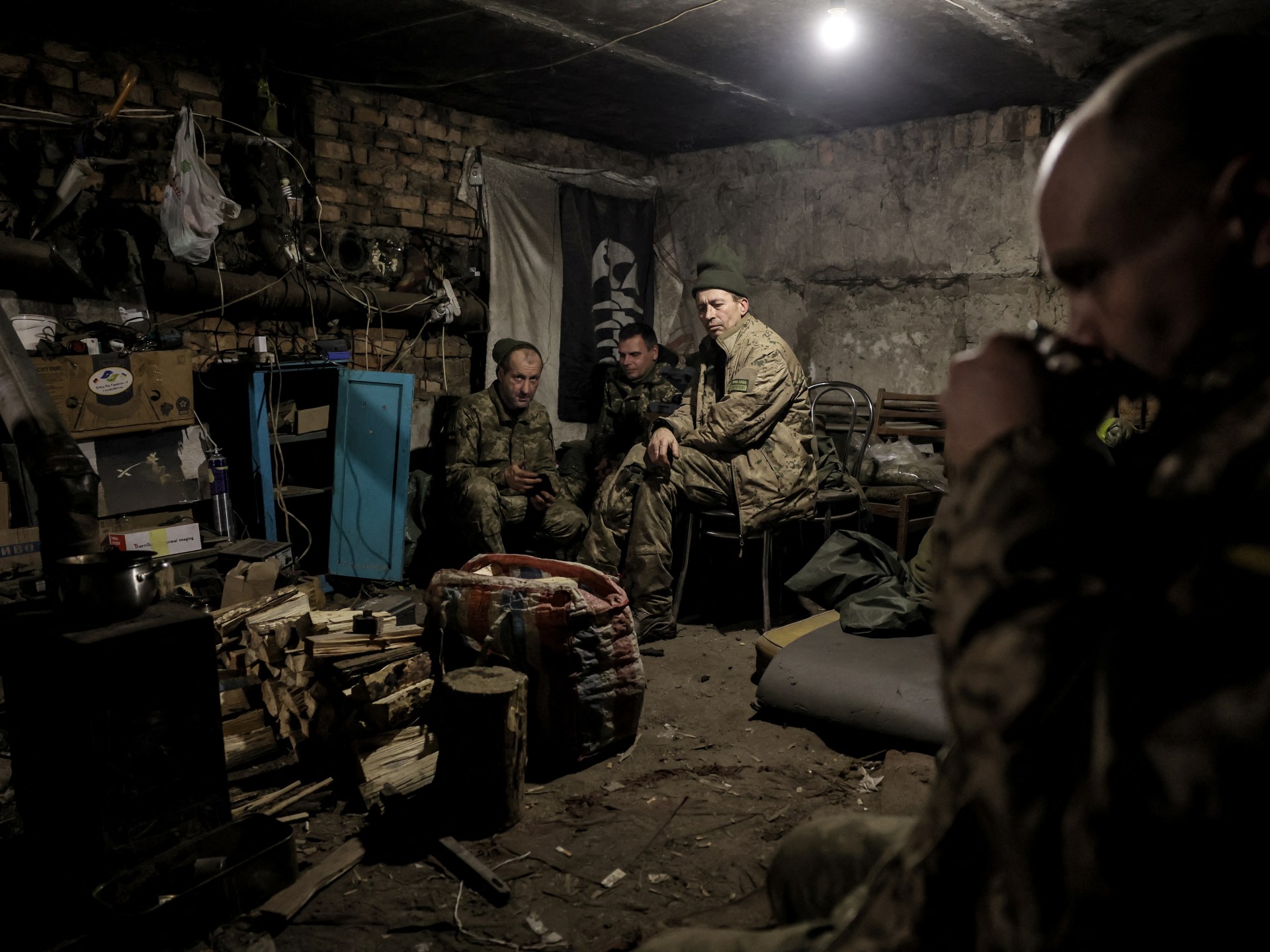


Kyiv, Ukraine – As Ukrainian forces fight in the western Russian region of Kursk, they are encountering a new enemy – elite North Korean servicemen.
On Sunday, Ukrainian infantry and armoured vehicles resumed an offensive in three directions in Kursk, trying to fence their toehold in the district centre of Sudzha that they had seized in August.
By Tuesday, they occupied at least three villages northeast of Sudzha – and inflicted losses on the North Koreans that fight in separate units under Russian command.
“We thinned their ranks – they have losses, although Kim didn’t just send ordinary servicemen,” a Ukrainian soldier told Al Jazeera, referring to North Korean leader Kim Jong Un.
He did not disclose his name, details and exact whereabouts of the battles in accordance with wartime regulations.

South Korean and US officials have said Kim deployed more than 10,000 elite soldiers to Kursk. Hundreds are understood to have been killed there already.
More than 450km (280 miles) south of Kursk, another Ukrainian serviceman keeps repelling waves of Russian infantrymen near the key southeastern city of Pokrovsk.
Advertisement
“Looks like they send a new brigade every day,” the serviceman told Al Jazeera.
Russians keep advancing despite a reported lack of tanks and armoured vehicles.
“They keep pushing. The only problem they have is their equipment, they can’t throw it around the way they did three or four months ago,” he said.
But the biggest problem his unit – as well as all of Ukraine’s armed forces – faces is a dire shortage of manpower.
Last week, Ukrainian troops retreated from the eastern town of Kurakhove, which Russian troops claimed control of on Monday.

Kyiv’s forces have also lost a key coal mine near Pokrovsk and could be about to lose Ukraine’s biggest lithium deposit in Shevchenkove.
“The Kurakhove defence installations have been taken over just because we didn’t have anybody there,” the serviceman said. “The most motivated soldiers have been killed, the new ones lack training and motivation.”
He also cited poor decisions made by commanding officers, alleging they want to appease their superiors and do not value the lives of servicemen.
“I’ve been wounded so many times because of the commanders’ stupidity,” he said.
Russians ‘looting’ in Donetsk town
The Russian forces that seized Kurakhove are looting abandoned apartments, a local woman alleged.
“They’re breaking into apartments that haven’t been damaged by shelling, they steal everything they can carry away,” Olena Basenko, a former sales clerk from Kurakhove who is looking for her elderly aunt who refused to leave the town, told Al Jazeera.
Advertisement
“Some ‘liberators’ they are,” she said sarcastically referring to Moscow’s pledge to “liberate” Ukraine from President Volodymyr Zelenskyy’s “neo-Nazi junta” – Russian claims that have been debunked throughout the war.
Ukraine’s shortage of manpower has led some analysts to doubt Kyiv’s push to resume the Kursk offensive.
“Zelenskyy’s strategy is to amass brigades with equipment in the rear only to solemnly lose them in the land of Kursk to gain 1.5km [1 mile] of farmland,” Nikolay Mitrokhin, a researcher with Germany’s Bremen University, told Al Jazeera.
The units that are advancing in Kursk could instead have been used to defend Kurakhove, he said.
However, others see the Kursk offensive as a chance to gain an important bargaining chip.

Ukraine may try to seize a Russian nuclear power plant in the town of Kurchatov that lies about 70km (45 miles) northeast of Sudzha and could attempt to seize Kursk’s regional capital 30km (20 miles) farther away.
If successful, the takeover of Kurchatov may become a significant strategic gain, according to the former deputy head of Ukraine’s general staff of armed forces.
“We didn’t want to make things worse, but we need to,” Lieutenant General Ihor Romanenko told Al Jazeera.
Advertisement
Kyiv may also invade the nearby Russian region of Bryansk, dealing a heavy blow to Russian President Vladimir Putin’s domestic reputation, he said.
“It will be painful to Putin, and if there is an offensive somewhere in Bryansk or some other regions, it will make him think,” Romanenko said.
Some Russians ridicule Putin’s policies that led to the first foreign invasion of western Russia since World War II.
“If the grandpa from the bunker is so wise, why do we have Ukrainians on Russian land? Something must be wrong,” Roman, a 48-year-old Muscovite who served in a tank unit in the 1990s, told Al Jazeera, deriding the Russian president.

Bryansk borders Ukraine and has been repeatedly attacked by two Ukrainian military units made up of pro-Ukrainian Russian fighters.
Romanenko said Putin’s decision to ramp up Russia’s offensive in southeastern Ukraine signifies a “fiasco” of Trump’s “peace plan”.
“This approach ended with a fiasco because Putin rejected the version proposed by Trump’s team,” he said.
Trump has offered few details of the plan, but, according to his team, it may include the establishment of a “demilitarised zone” along the current front line, Kyiv’s ceding of Russia-occupied areas and a delay of Ukraine’s NATO membership.
Advertisement
Ukraine’s sea drone weapons
At the end of last year, Ukraine scored a small victory that may herald huge losses in Russian navy bases and civilian seaports.
On December 31, Ukrainian sea drones, or un-piloted vessels armed with small missiles, attacked Russian helicopters in the bay of Sevastopol, the main naval base in annexed Crimea.
Ukraine claimed to have shot down two helicopters, killing all 16 crew members.
Moscow acknowledged no losses but said its forces destroyed four Ukrainian unmanned aircraft and two sea drones.
The attack showed that sea drones could wreak havoc on Russian port and naval infrastructure along the Black Sea, Bremen University’s Mitrokhin said.
Furthermore, Kyiv could use sea drones for attacks on the Russian navy in the Baltic, Barents and White Seas and in the Pacific.
“There is so much infrastructure there that it will be hard to cover it even with boom barriers, let alone protect them from all sides like in Sevastopol or [the Crimean port of] Feodosiya,” he said.

Meanwhile, the ongoing war of attrition tests Ukraine and Russia’s economies.
The Russian economy has “partially adapted to the pressure from [Western] sanctions, but it currently enters the inflation shock of overheating and slower growth” because of the Central Bank’s high percentage rates, Kyiv-based analyst Aleksey Kusch said.
Advertisement
The Ukrainian economy is “in shock” because of severely damaged energy infrastructure and a lack of labour force, he said.
But hydrocarbon exports help Russia’s economy recover from the shock, while Ukraine is kept afloat by Western financial aid.
“It creates a certain parity effect amid resistance to war,” Kushch told Al Jazeera.

Related News
Biden cancels another $4.2bn in US student loans before leaving office
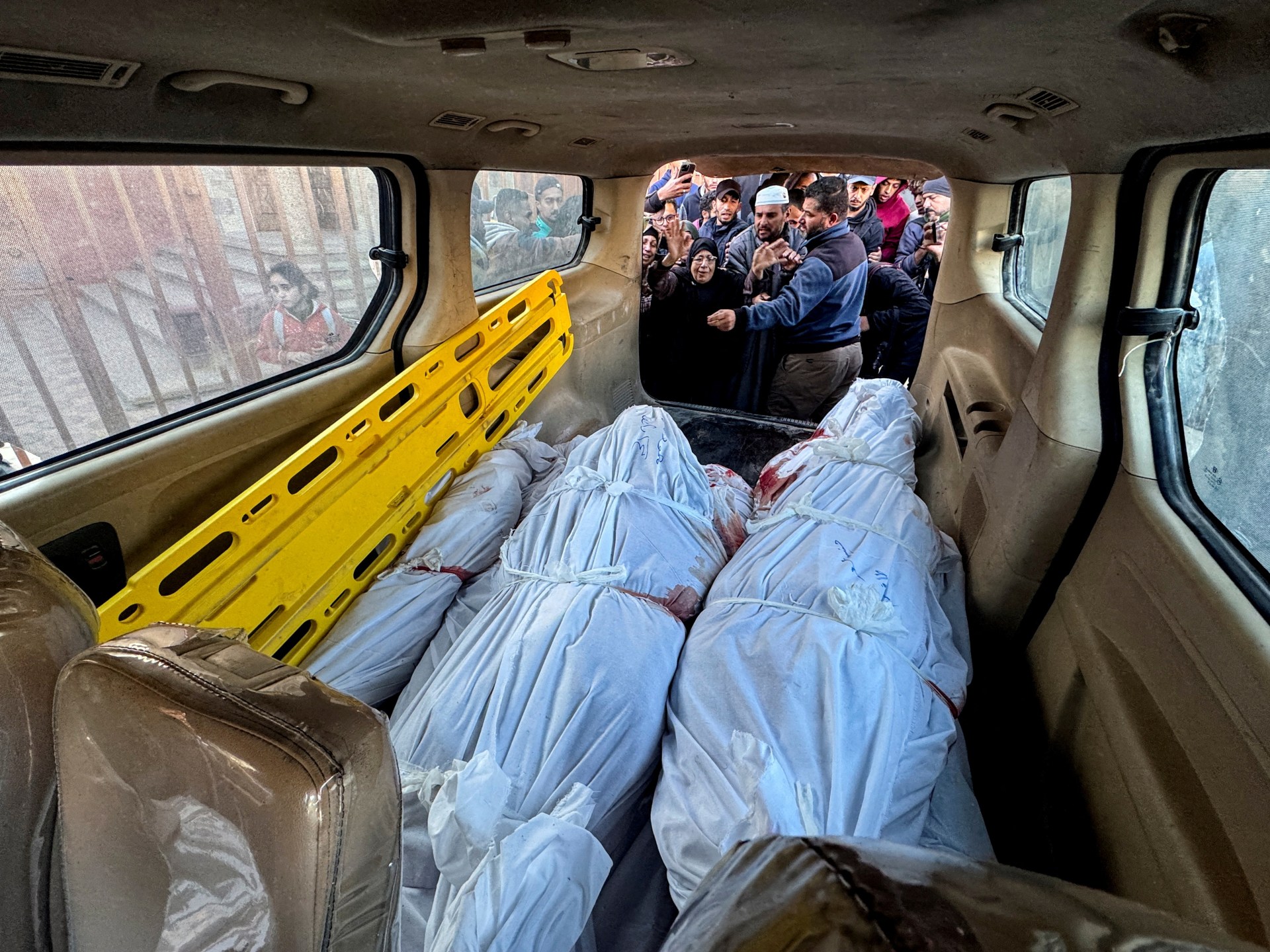

Israel’s army again targets Kamal Adwan Hospital as Gaza toll passes 45,000
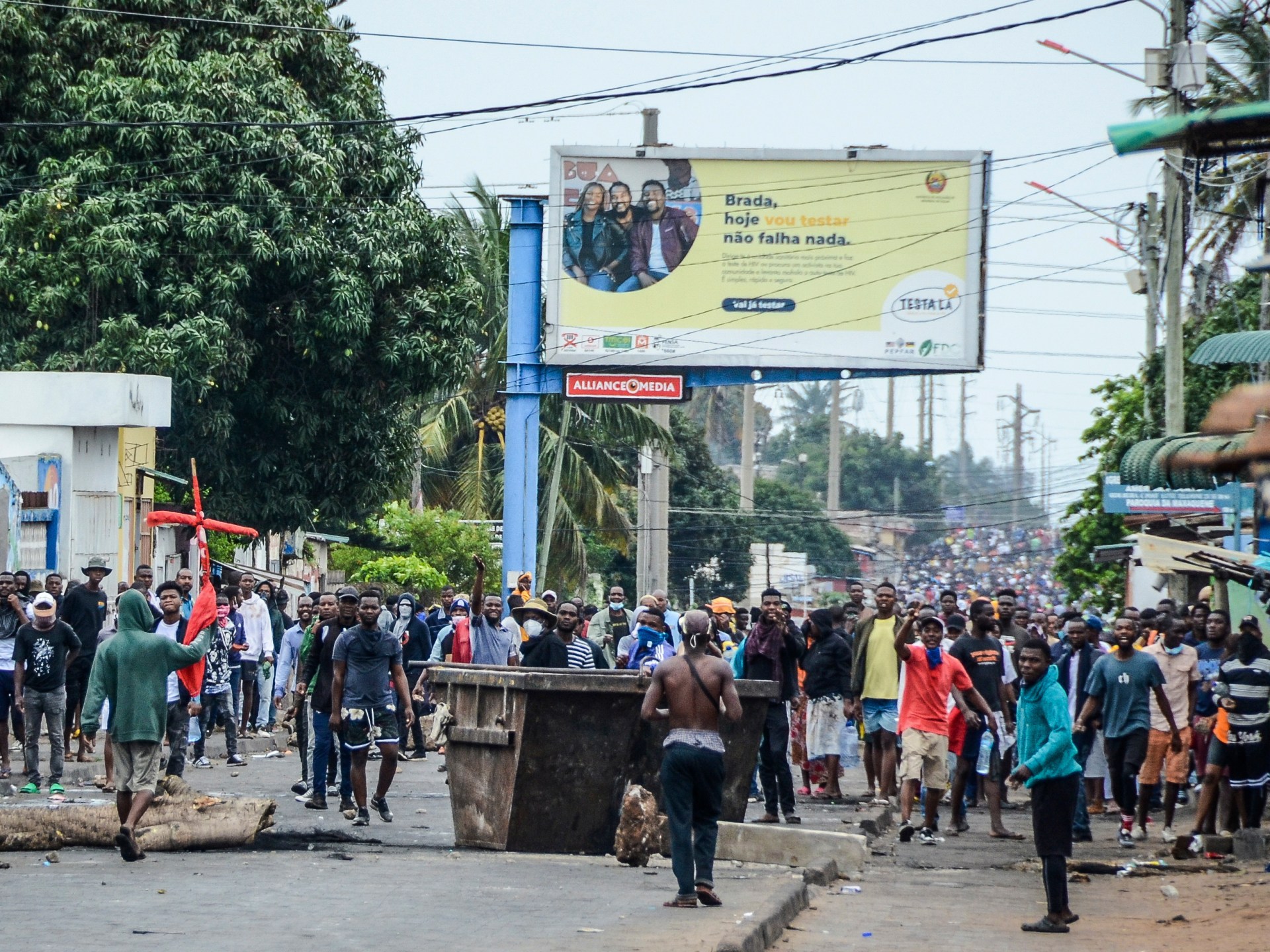

At least 21 killed in Mozambique unrest after top court’s election decision

